Repairing & Avoiding Electronic Faults with Thermal Paste
18 September 2023
Thermal grease, also known as thermal paste or thermal compound, is a substance used to improve the thermal conductivity between two surfaces, typically between a microprocessor and a heat sink. The purpose of thermal grease is to fill in the microscopic gaps and imperfections on the surface of the microprocessor and the heat sink, which would otherwise create an insulating layer of air between the two surfaces.
By filling in these gaps, thermal grease allows for better heat transfer from the microprocessor to the heat sink, which helps to prevent overheating and prolong the lifespan of the electronic device. This is particularly important in high-performance electronics, such as industrial PC, gaming computers, servers, and graphic cards, which generate a lot of heat.
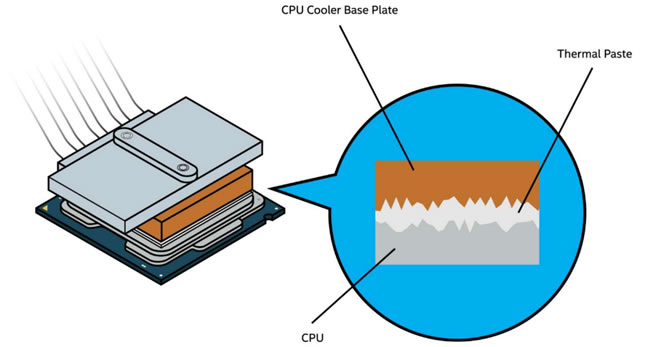
Why you need Thermal paste [1]
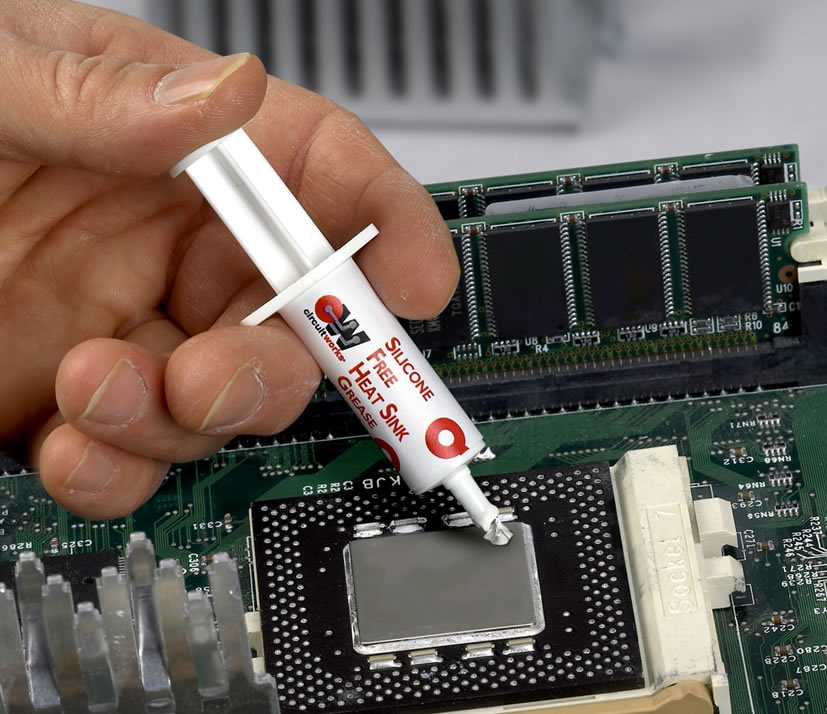

Technician applying thermal paste to the CPU
What Are the Types of Thermal Grease?
There are several types of thermal greases available, including silicone-based, metal-based, and ceramic-based compounds. The choice of thermal grease depends on the specific application, with some compounds being better suited to high-temperature environments or providing better thermal conductivity.
Silicone-based thermal grease: Silicone-based thermal grease is a popular type of thermal grease that is commonly used in the electronics industry. It is a non-conductive material that has good thermal conductivity and can withstand high temperatures. It is easy to apply and remove, making it ideal for use in applications that require frequent maintenance or replacement.
Metal-based thermal grease: Metal-based thermal grease is a type of thermal grease that contains metal particles, such as copper, silver, or aluminum. These particles improve the thermal conductivity of the grease, making it more effective at transferring heat away from electronic components.
Ceramic-based thermal grease: Ceramic-based thermal grease is a type of thermal grease that contains ceramic particles, such as boron nitride or aluminum oxide. These particles provide high thermal conductivity and excellent thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Ceramic-based thermal grease is typically more expensive than other types of thermal grease but can provide superior performance in extreme environments.
Carbon-based thermal grease: Carbon-based thermal grease is a type of thermal grease that contains carbon particles. These particles provide good thermal conductivity and are less expensive than metal or ceramic-based thermal grease. Carbon-based thermal grease can be used in a variety of applications but may not be as effective as other types of thermal grease in high-temperature environments.
Phase-change thermal grease: Phase-change thermal grease is a type of thermal grease that changes from a solid to a liquid state when it reaches a certain temperature. This allows it to conform to the surface of electronic components and provide excellent thermal conductivity. Phase-change thermal grease is typically more expensive than other types of thermal grease and can be difficult to apply and remove.
Graphene-based thermal grease: Graphene-based thermal grease is a relatively new type of thermal grease that contains graphene particles. Graphene has excellent thermal conductivity and can provide superior heat dissipation compared to other types of thermal grease. Graphene-based thermal grease is typically more expensive than other types of thermal grease and may require specialized equipment for application.
Where Should You Use Thermal Paste?
Thermal grease is typically used in applications where electronic components generate a significant amount of heat and require cooling. Here are some common applications where thermal grease may be used:
- CPU cooling - Thermal grease is commonly used to improve the thermal conductivity between the CPU and the heat sink in desktop computers and laptops.
- GPU cooling - Graphics processing units (GPUs) generate a lot of heat and require effective cooling, which can be improved with the use of thermal grease.
- Power supply units - The power supply unit (PSU) of a computer can also benefit from thermal grease, which can help to dissipate heat generated by components such as transformers and capacitors.
- LED lighting - Thermal grease can improve the heat dissipation in LED lighting, reducing the risk of overheating and increasing the lifespan of the components.
- Solid-state drives - High-speed solid-state drives (SSDs) generate a lot of heat, and thermal grease can be used to improve heat transfer between the controller chip and the drive casing.
- Audio amplifiers - Amplifiers generate heat when operating at high volumes, and thermal grease can be used to improve heat transfer between the components and the heat sink.
- Automotive electronics - Thermal grease can be used in automotive electronics, such as engine control units (ECUs) and navigation systems, to improve heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Industrial equipment - Industrial electronics, such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and motor control systems, can benefit from thermal grease to improve thermal management and prevent component failure.
- Medical equipment - Thermal grease can be used in medical equipment, such as ultrasound machines and CT scanners, to improve heat dissipation and prevent overheating.
- Aerospace electronics - Electronics used in aerospace applications, such as flight control systems and communication systems, require effective thermal management to operate reliably in harsh environments, and thermal grease can play a role in achieving this.
What Type of Faults Can Be Fixed or Avoided with Thermal Paste?
Here are different types of faults in industrial electronics that can be cured or prevented with thermal grease:
- Overheating of electronic components - The excessive heat generated by industrial electronic components can cause them to overheat and fail. Applying thermal grease can help to improve heat dissipation and reduce the risk of component failure due to overheating.
- Thermal expansion and contraction issues - As electronic components heat up and cool down, they can expand and contract, causing stress on the connections between components. Applying thermal grease can help to reduce the stress and prevent damage to the components.
- Vibration-induced damage - In industrial environments, electronic components can be subject to vibration, which can cause damage to the components over time. Applying thermal grease can help to reduce the effects of vibration by providing better contact between the components.
- Noise issues - Fans and other cooling components can sometimes generate noise, which can be caused by vibration or inadequate cooling. Applying thermal grease to the relevant components can help to reduce noise by improving heat transfer and preventing excessive heat buildup.
- Corrosion - Corrosion can damage electronic components and cause them to fail. Applying thermal grease can help to prevent corrosion by protecting the components from exposure to moisture and other corrosive elements.
- Contamination - Industrial environments can be dirty and dusty, which can lead to contamination of electronic components. Applying thermal grease can help to seal the components and prevent contamination from affecting their performance.
- Inadequate cooling - Inadequate cooling can cause industrial electronics to overheat and fail. Applying thermal grease can help to improve the cooling of the components and prevent overheating.
- Temperature cycling - Temperature cycling can cause stress on electronic components and lead to failures. Applying thermal grease can help to reduce the stress caused by temperature cycling and prevent damage to the components.
- Environmental factors - Industrial electronics can be exposed to a wide range of environmental factors, such as humidity, temperature, and vibration. Applying thermal grease can help to protect the components from these factors and improve their reliability and longevity.
How Do You Apply Thermal Paste?
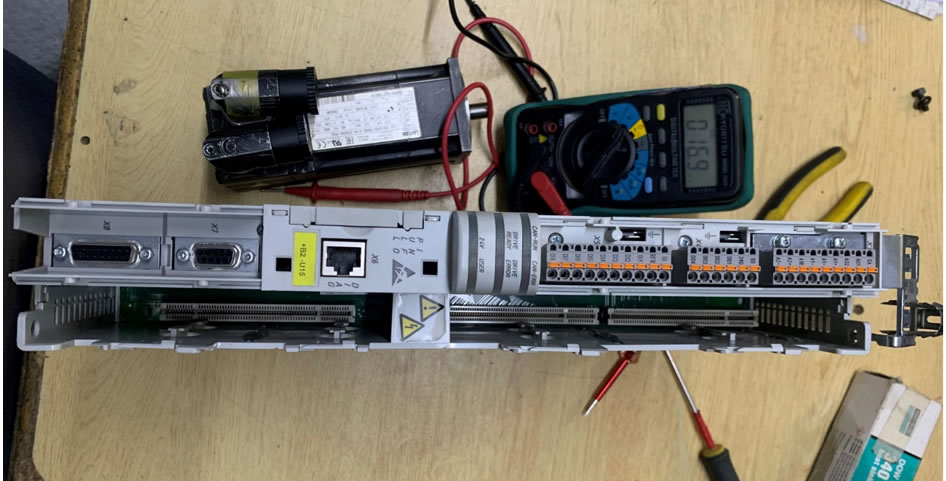
Here are the steps to apply thermal grease on electronic components, based on an actual repair job. A Lenze servo drive 9400 on TEXPA DUVET machine was stopping after 10 hours of continuous operation due to overheating in the IGBT Module.
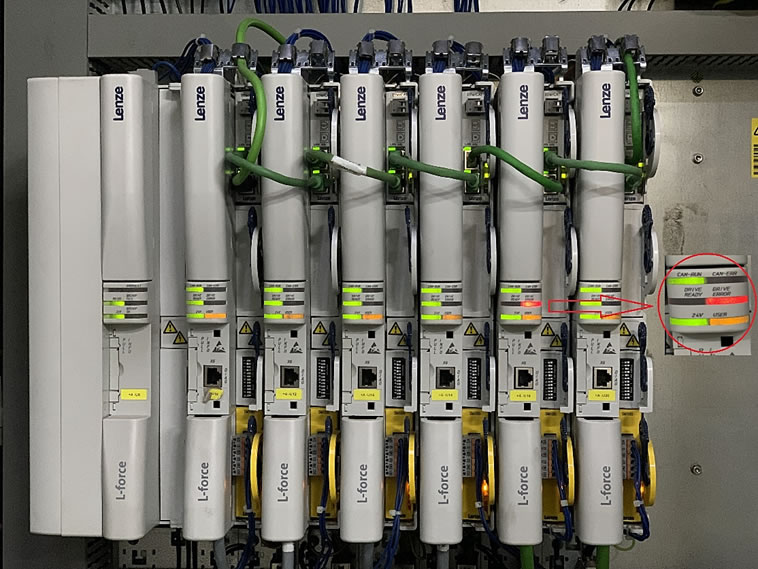

Lenze 9400 servo drives installed in multi rack system
After carefully removing the drive from multipoint rack, I dismantled the parts and determined the thermal grease in the IGBT module had dried up which hindered the flow of heat from module toward the heat sink. Following are the steps to resolve this issue.
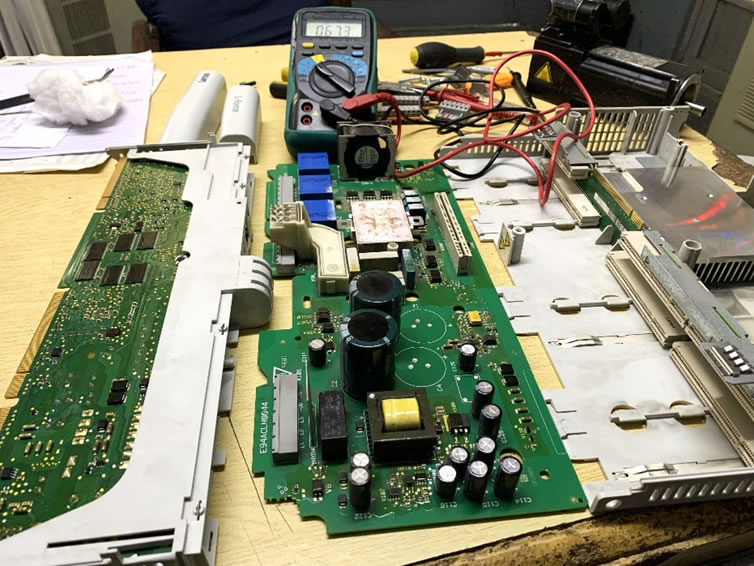

Dismantle the Drive for the purpose of faults diagnosing.
Clean the surface: Before applying thermal grease, clean the surface of the electronic component and the heat sink to remove any dust, dirt, or debris.
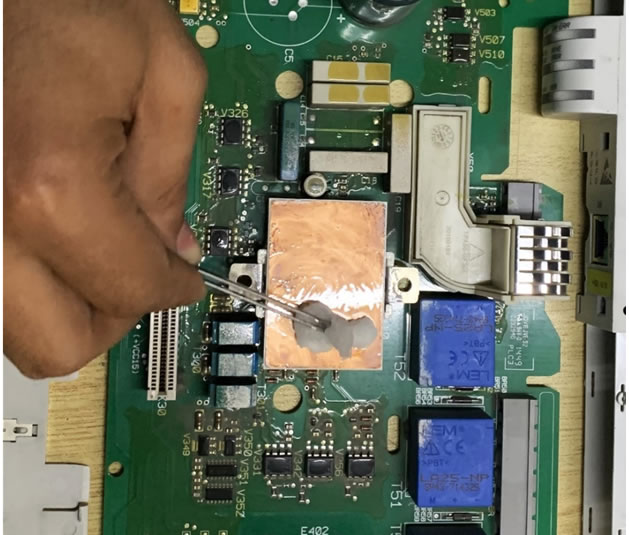
Clean the metal contact of IGBT Power Module
Apply a small amount of thermal grease: Using a clean applicator, apply a small amount of thermal grease on the surface of the electronic component. Be careful not to apply too much grease, as this can cause excess heat buildup and reduce the effectiveness of the cooling system.
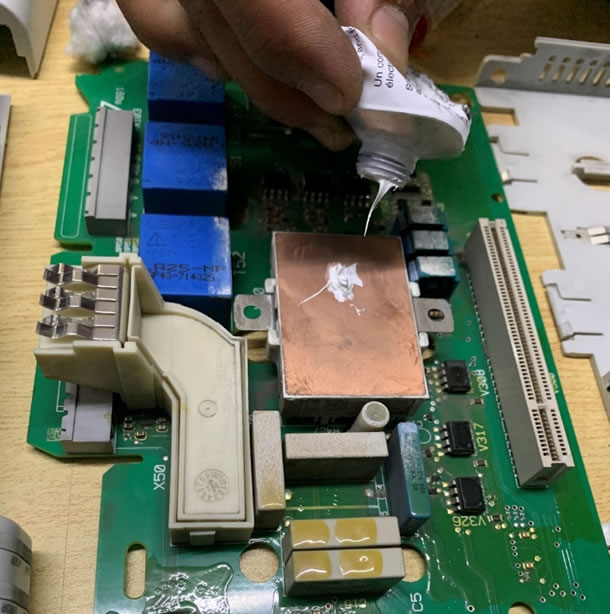

Apply a small amount of Thermal Paste
Spread the grease evenly: Use a flat tool, such as a plastic or metal spatula, to spread the thermal grease evenly over the surface of the electronic component. The layer of grease should be thin and uniform, with no air pockets or gaps.
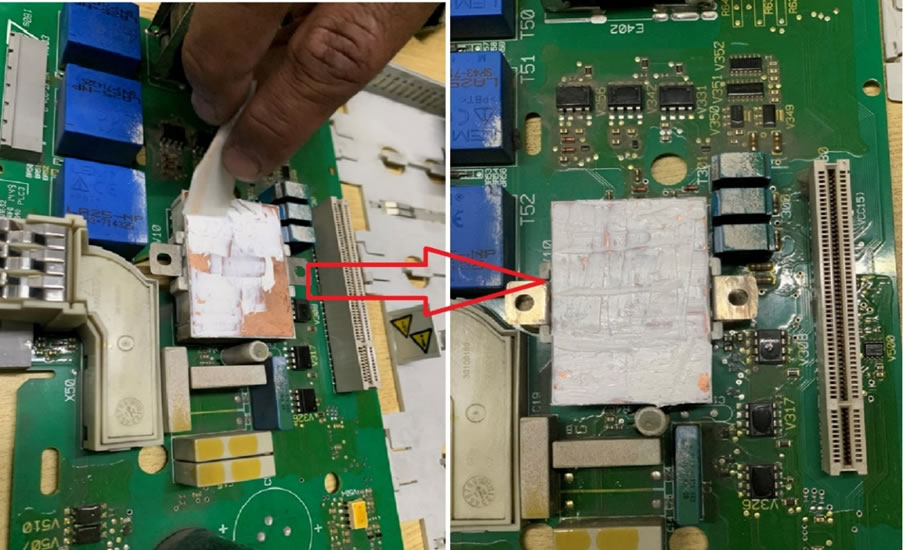
Spread the paste equally on the body of IGBT Module
Install the component: Once the thermal grease has been applied, install the electronic component onto the heat sink or cooling device. Make sure the component is securely fastened and that the thermal interface material is making good contact with the heat sink.
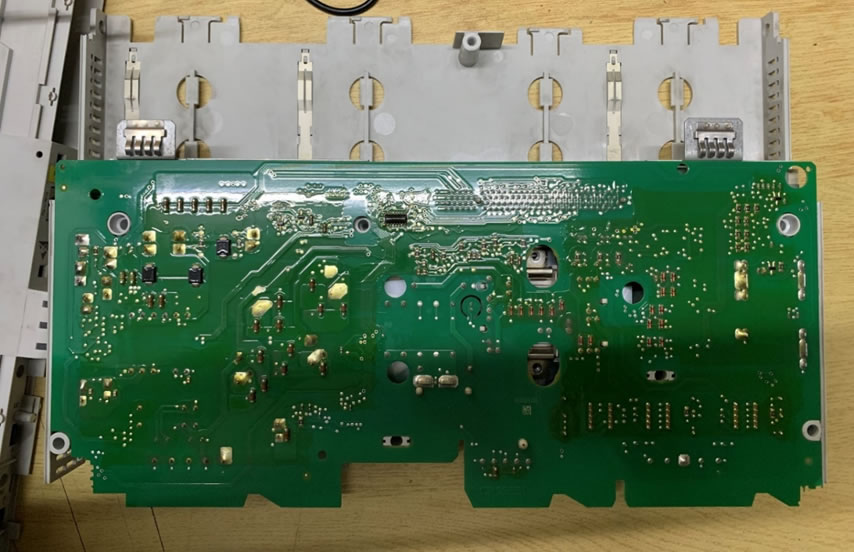
Install the heatsink on power Module and tighten the screws
Reassemble the remaining parts of the drive
Clean up any excess grease: Clean up any excess thermal grease using a clean cloth or paper towel. Avoid leaving any excess grease on the surface of the electronic component, as this can cause it to overheat and fail.
Test the system: After applying the thermal grease, test the cooling system to ensure that it is working properly and that the electronic components are not overheating. If necessary, adjust the amount of thermal grease or the cooling system settings to achieve optimal performance.
Precautions: Applying thermal grease requires precision and care, as too much or too little can adversely affect the performance of the electronics. The correct amount of thermal grease is typically a thin layer, applied evenly to the microprocessor, power modules and other electronic components before installing the heat sink.
Why Do I Need to Use Thermal Paste?
There are several possible faults in electronics that can be caused by overheating or damage within the electronics which can be prevented by using thermal paste:
- Reduced lifespan of components - When electronic components, such as transistors and capacitors, are exposed to high temperatures for extended periods, their lifespan can be significantly reduced. This can lead to component failure and potentially even damage to other components.
- Thermal expansion - As electronic components heat up, they expand. This can cause physical stress on the components and potentially lead to cracking or other damage.
- Circuit board damage - When circuit boards are exposed to high temperatures, the solder that connects components to the board can melt and cause damage to the board. This can lead to connection failures or even complete board failure.
- Thermal runaway - Some electronic components, such as certain types of diodes, can experience thermal runaway when they get too hot. This means that the component will continue to heat up even after the heat source is removed, potentially leading to component failure or even a fire.
- Reduced performance - When electronic components get too hot, their performance can be negatively impacted. This can result in slower operation or even complete system failure.
To avoid these faults, it is important to keep electronics within their safe operating temperature range and to properly ventilate and cool electronic devices. Using thermal paste in appropriate situations can prevent some of these common outcomes.


Leave your comment